This is the sum total of all the reactions occurring in the cells.
reactions include the breakdown of glucose to CO2 and H2O.
These reaction take place in a series of steps e.g reactants----- intermediates-----products
Each reaction in a pathways is catalysed by an enzyme.
The products can act as an inhibitor of an enzyme so it can control its own production.
Catabolism: the breakdown of complex molecules into smaller ones e.g. break down of glucose
This usually creates ATP
Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simple ones. e.g. joining amino acids together.
this usually uses ATP
The cell has two ways of controlling metabolic reaction:
1) compartmentalisation e.g. reactions take place in specific areas of the cell
2) enzymes, which can be inhibited by their products.
OXIDOREDUCTASES catalyse oxidation and reduction
HYDROLASES catalyse hydrolysis reactions e.g. breaking molecules byt he addition of water. used in : digestion etc
cellular respiration
All living organisms require energy for three major reasons:
1) for mechanical work e.g. muscle contraction
2) the active transport of ions across cell membranes
3) the synthesis of macromolecules
This 'free' energy is obtained from the environment.
Cellular respiration is the oxidation of food substances to obtain 'free' energy. Free energy can be used to drive reaction that require an input of free energy, such as active transport.
It occurs as a series of linked, enzymes catalysed reactions.
1) Gylcolysis
2) Krebs cycle
3) oxidative phosphorylation
Atp- Adenosine Triphosphate
this is the most important product of cellular respiration.
Used at an immediate source of free energy rather than a long term store. Its rate of production is high and usually used with 1 minute of synthesis.
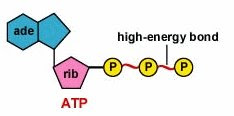
adenosine-ribose(5 carbon sugar)-3 inorganic phosphate groups
This is important because the phosphoanhydride bonds yield a high amount of free energy when hydrolysed.Atp can be hydrolysed to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and Pi and hydrogen.
ATP+ H2O---> ADP + P(i) + H(+)
deltaG= -30 kj mol-1

This is an exergonic reaction as it yields free energy.
ATP is quickly resynthesised from the products when food substances are oxidised in chemotropic organisms or due to light trapping on photosynthetic organisms.
Electron Carries
Many reactions in metabolic pathways require the removal of electrons or hydrogen atoms in the oxidation of substrates.
The electrons are transferred to a group of substances known as electron carriers (aka coenzymes or hydrogen carriers)
The reduced form of these carries transfer their electrons to oxygen by a chain of electron carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane. ATP is formed from ADP and Pi as a result.
NAD(+) = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
when a substrate is oxidised NAD accepts a hydrogen ion and 2 electrons. the reduced form is NADH. only 1 hydrogen atom is passed on
NAD(+) + 2H(+) + 2e(-) ----> NADH + H(+)
overview:
1) Intake of Food substances
2) substrate oxidised (oxidation removes hydrogen and electrons)
3)NAD(+)---reduced by addition of hydrogen and electrons to NADH
4)These reduced forms transfer their electrons to oxygen in the inner mitochondrial membrane
5) ATP is produced as a result of the energy released in the process below. the energy is used to generate another process in the cell to make atp.
(2NADH + 2H+ + O2 ==> 2NAD+ + 2H2O) dont have to learn!
Glycolysis
This occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and is a series of enzyme-catalysed reactions in which each molecule of glucose is turned into 2 molecules of pyruvate.
Pyruvate: a compound containing 3 carbon atoms and links glycolysis to the next reaction.
glucose + ATP ------(hexokinase)-------> glucose 6-phosphate + ADP + H(+)
Phosporylation of glucose:
1)prevents glucose from leaving the cell, as the membrane is impermeable to sugar phosphates.
2) it makes glucose more reactive
summary:
 Two 3-carbon compounds of Pyruvate are made from each molecule of glucose.
Two 3-carbon compounds of Pyruvate are made from each molecule of glucose.
2 molecules of ATP used but 4 produced in glycolysis.
NET PRODUCTION :TWO MOLECUlES OF ATP
Pyruvate then passes into a mitochondrion and then the krebs cycle occurs.
Aerobic Respiration(oxygen present)
The krebs cycle
Pyruvate + NAD(+) + CoA ---------> Acetyl CoA + NADH + CO2
4 carbon compound combines with with two carbon acetyl to form acetyl CoA, this forms a 6 carbon compound citrate.
2 atoms are lost in each turn of the cycle. These are lost as CO2.
NAD reduced and FAD
Hydrogen is lost
summary:
Two carbon atoms enter the carbon cycle and two carbon are lost as carbon dioxide
one molecule of ATP is formed
4 pairs of hydrogen are removed
3 NAD's are reduced and 1 FAD is reduced
The reduced electron carriers are reoxidised in the electron transport chain.
 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
this is the process by which atp is made. ATP is formed when electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen.NADH oxidation produces 3 ATP, FADH2 oxidation produces 2 ATP.
Each [H] atom splits into [H+] and [e-]
The transfer of electrons to oxygen through electron carriers leads to [H+] being pumped from the matrix into the inter membrane space. when they flow back into the matrix the free energy made avaliable is used to make ATP.
Electrons are transfered from NADH to oxygen through a series of large protein complexes.

Oxygen acts as the final electron recpetor and is reduced to form the final product which is , water.
ATP YIELD: 36 molecules from one glucose molecule.
Anerobic respiration:
the electron transport chain cannot function without oxygen. Respiring anerobically poses a problem as they need to reoxidise electron carriers.
used during vigorous physical exertion.
Pyruvate is reduced to Lactate and NAD so glycolysis can continue.
lactate accumulates in the muscles and after exercise lactate is oxidised back to pyruvate.
In yeast it ends up with ethanol and CO2 produced, the yield of ATP is two molecules from one molecule of glucose.
--
